

See-Docs & Thenavigo
Getting Started with NodeJs
Node.js is an open-source JavaScript software platform designed for highly competitive, event-driven network applications that need to scale.
As an asynchronous event-driven JavaScript runtime, Node.js is designed to build scalable network applications. In the following "hello world" example, many connections can be handled concurrently. Upon each connection, the callback is fired, but if there is no work to be done, Node.js will sleep
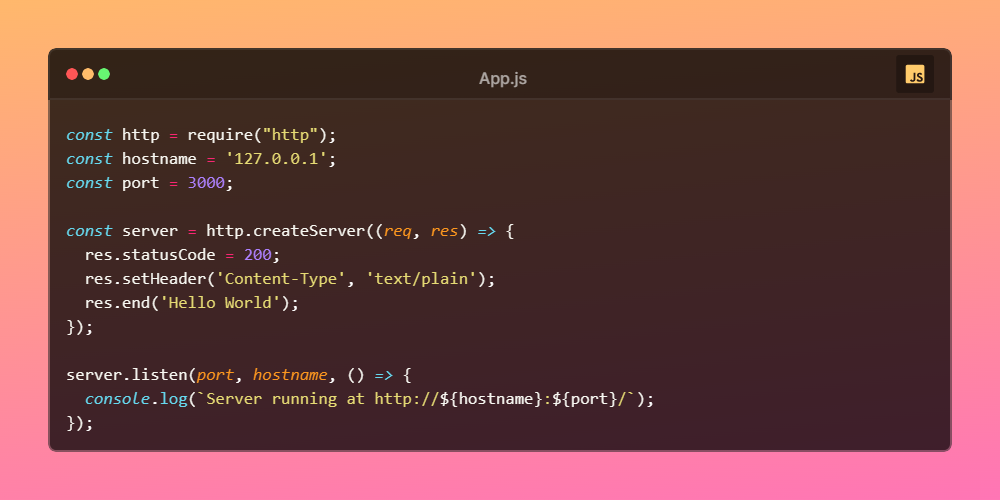
- Node is a runtime environment for executing JS code.
- Essentially, Node is a C++ program that embeds Chrome’s v8 engine, the fastest
JS engine in the world.
- We use Node to build fast and scalable networking applications. It’s a perfect
choice for building RESTful services.
- Node applications are single-threaded. That means a single thread is used to
serve all clients.
- Node applications are asynchronous or non-blocking by default. That means
when the application involves I/O operations (eg accessing the file system or the
network), the thread doesn’t wait (or block) for the result of the operation. It is
released to serve other clients.
- This architecture makes Node ideal for building I/O-intensive applications.
- You should avoid using Node for CPU-intensive applications, such as a video
encoding service. Because while executing these operations, other clients have
to wait for the single thread to finish its job and be ready to serve them.
- In Node, we don’t have browser environment objects such as window or the
document object. Instead, we have other objects that are not available in
browsers, such as objects for working with the file system, network, operating system, etc.

See-Docs & Thenavigo
Thenavigo: We share relevant learning content for People.